#16 Spotify - The digital music giant from Sweden
Dive deep into Spotify's business model and financials
Dear readers,
thank you for being here and for your interest in my work! If you like this article, if you find this stock watchlist and my deep dives valuable, and if you want to support my work, please feel free to subscribe!
Please read the disclaimer at the end of this article. This is not investment advice!
Introduction
I've been encountering numerous discussions about Spotify SPOT 0.00%↑ lately, and as a premium customer myself, my interest in the platform extends beyond just enjoying its offerings. I regularly turn to Spotify for music during workouts and podcasts for my commute. The company's stock performance caught my attention too; it soared over 100% in 2023 alone. However, since its IPO, the overall gain stands at around 26% – a CAGR of 4.2%. This intriguing contrast between its product success and stock performance piqued my curiosity, prompting me to delve deeper into Spotify's business dynamics. Join me as we embark on this comprehensive exploration!
Overview of Spotify and Market
Spotify's mission is to unleash human creativity by enabling a million artists to earn a living from their art and allowing billions of fans to enjoy and be inspired by it. As of September 30, 2023, Spotify is the leading global audio streaming subscription service, with 574 million Monthly Active Users (MAUs), including 226 million Premium Subscribers, across 184 countries.
The global recorded music industry has been growing since its shift from physical sales to streaming models, with significant revenue increases year-over-year, particularly in streaming. Spotify, a major contributor to this growth, has paid over €34 billion in royalties to record labels, music publishers, and rights holders since its inception, marking a substantial impact on the music industry's revenue.
Spotify has revolutionized music and podcast access, offering over 100 million tracks and 5 million podcast titles. The platform has recently ventured into audiobooks, expanding its content library. This move from a transaction-based to an access-based model differs from traditional radio's linear distribution, providing users with a vast choice and on-demand streaming.
The company invests in podcasts and alternative content, enhancing the user experience and engagement. Exclusive content agreements further differentiate Spotify's service. The platform focuses on discovery, guiding users to new entertainment experiences and leveraging user data to create cultural narratives. Spotify's approach aims to drive customer satisfaction, engagement, and continual discovery,
solidifying its position not just as a streaming service, but as a key player in the discovery and enjoyment of diverse audio content. This strategy is designed to attract new users, keep current users engaged, and continually expand the influence of music, podcasts, and other audio content in people's lives.
The global recorded music industry has been experiencing significant growth, primarily driven by streaming services. After a decade-long decline due to the shift from physical sales to digital streaming, the industry reached a turning point in 2015 and has been growing steadily since. In 2021, global recorded music revenues increased by 18% to $26 billion, continuing a trend of yearly growth since 2015. Notably, streaming revenues, which grew by 24% in 2021, now constitute over 65% of total global recorded music revenues.
As the leading global audio streaming subscription service, Spotify plays a crucial role in this growth. The company has contributed significantly to the increase in global recorded music revenue, having paid more than €34 billion in royalties to record labels, music publishers, and other rights holders as of December 31, 2022. In 2022 alone, Spotify's expenses for rights holders increased by 21% compared to the previous year, underscoring its impact as a major revenue source for artists and labels in the music industry.
Business Model and Strategy
Spotify is developing a two-sided marketplace that benefits both users and creators. This strategy leverages Spotify's relationships, data analytics, and software, reshaping how users enjoy, discover, and share audio content. By providing creators with insights and new tools, Spotify empowers them with more control and monetization opportunities. This approach allows creators and fans to connect directly and helps creators understand and engage their audience effectively.
Regarding its business model, Spotify offers both Premium and Ad-Supported Services. The Premium Service provides unlimited streaming of music and podcasts without ads, and subscribers can purchase audiobooks in certain markets. This service is accessible across various devices and offers multiple subscription plans to cater to different demographics. The Ad-Supported Service, meanwhile, offers limited on-demand access to music and unlimited podcast access, serving as a channel to acquire Premium Subscribers and a standalone product for those who prefer free access.
Spotify's Premium segment revenue comes from subscription sales, including partnerships with telecommunications companies. The number of Premium Subscribers, which stood at 226 million as of September 30, 2023, is a key revenue driver. This growth is partly due to converting Ad-Supported Users to Premium Subscribers through marketing and trial programs.
The Ad-Supported segment generates revenue mainly from the sale of advertising across music and podcast content. Spotify collaborates with advertising agencies and directly with large advertisers, selling ads based on the cost-per-thousand impressions model. This segment's revenue depends on user engagement and the effectiveness of its advertising products.
In February 2021, Spotify launched the Spotify Audience Network (SPAN), an audio advertising marketplace connecting advertisers with listeners across various podcasts. This network supports targeted advertising and revenue sharing with partners. Overall, Spotify's strategy focuses on expanding its advertising product portfolio and enhancing advertising revenue through innovative approaches and analytics.
Business Segments and Licensing Agreements
Spotify operates its business through two primary segments: Premium and Ad-Supported, each contributing to the company's revenue generation.
Premium Segment:
Service Offering: This segment provides subscribers with unlimited online and offline high-quality streaming access to Spotify's extensive music and podcast catalog. Additionally, premium subscribers can purchase audiobooks á la carte in select markets.
Device Compatibility: The service is accessible on a variety of devices including computers, tablets, mobile devices, speakers, televisions, cars, game consoles, and smart devices, offering an ad-free listening experience.
Revenue Generation: Revenue comes from subscription sales, either directly to end-users or through partnerships with telecommunications companies and other partners. Different subscription plans are offered, including Standard, Family, Duo, and Student plans, catering to diverse user preferences and demographics. Pricing is adapted to local markets.
Subscriber Growth and Retention: As of December 31, 2022, Spotify had 205 million premium subscribers. Growth in this segment is driven by converting ad-supported users to premium subscriptions through marketing efforts and trial programs. Retention rates have improved over time, aided by diverse subscription plans and enhanced service features.
Ad-Supported Segment:
Service Features: This segment offers users limited on-demand online access to music and unlimited access to podcasts without a subscription fee. Users in this segment can also purchase audiobooks on an á la carte basis.
Revenue Model: Revenue is primarily generated from display, audio, and video advertising sold on a cost-per-thousand basis. Spotify collaborates with advertising agencies and large advertisers, and revenue is recognized based on the number of impressions delivered.
Advertising Strategy: Spotify's strategy emphasizes relevant advertising products for music and podcast listeners to enhance user experience and advertiser returns. In 2021, Spotify introduced the Spotify Audience Network (SPAN), an audio advertising marketplace that further expands its advertising capabilities.
Revenue Recognition:
For Premium Revenue: Subscription revenue is recognized on a straight-line basis over the subscription period, with partner subscription revenue based on per-subscriber rates in partner agreements.
For Ad-Supported Revenue: Revenue is recognized as impressions are delivered on the platform, with arrangements including automated exchanges, internal self-serve, and advertising marketplace platforms.
Spotify secures the necessary intellectual property rights to stream content through various licensing agreements with rights holders. Here's a summary of these agreements:
Sound Recording License Agreements: Spotify has agreements with major music companies like Universal Music Group, Sony Music Entertainment, Warner Music Group, and Merlin, which represents independent labels. These agreements typically include royalty payments, marketing commitments, and data reporting obligations. Approximately 75% of the audio content streamed in 2022 was under these agreements, which are multi-year, non-automatically renewable, and have worldwide application.
Musical Composition License Agreements: Spotify obtains licenses for mechanical and public performance rights. In the U.S., rates are set by the Copyright Royalty Board and apply to both compulsory licenses and direct licenses with music publishers. Spotify has a new blanket license under U.S. law, administered by the Mechanical Licensing Collective. Rates are subject to change by the Copyright Royalty Board and are forecasted by Spotify based on management estimates. Public performance rights are typically obtained through performing rights organizations (PROs) like ASCAP, BMI, GMR, and SESAC.
Podcast License Agreements: Spotify negotiates licenses directly with podcasters and podcast networks or obtains rights through its owned platforms like Anchor and Soundtrap for Storytellers. These agreements often involve multi-year commitments and may include revenue sharing and minimum guarantees.
Audiobook License Agreements: Similar to podcasts, Spotify negotiates licenses for audiobooks directly with publishers or authors or through its platform, Findaway Voices. Rights for audiobook production and distribution are also obtained from book publishers and authors.
License Agreement Extensions and Renewals: Spotify may extend or provisionally continue licenses as negotiations for renewal occur. The continuation of content availability is subject to these extensions or provisional licenses.
These licensing agreements are crucial for Spotify's operation, enabling it to legally stream a vast array of content. However, the dependency on third-party licenses poses risks, as changes, losses, or claims regarding these licenses could adversely impact Spotify's business and operations.
Spotify incurs royalty costs to stream music, which are paid to record labels, music publishers, and other rights holders. These royalties are calculated using various methods: negotiated rates per license agreements, estimates for unidentified rights holders, or rates set by government bodies. The process involves significant judgments, assumptions, and estimates due to complex agreements and numerous variables.
Key Points on Royalty Costs and Licensing Agreements:
Royalties are based on revenue (Premium and Ad-Supported) or user/usage measures.
In some jurisdictions, rights holders may claim royalties several years after streaming, leading to estimated royalty costs.
Royalties for content used while negotiating agreements are based on Spotify's best estimate of eventual payouts.
Due to a vacated ruling by the U.S. Court of Appeals in 2020 regarding royalty rates for mechanical rights, Spotify's royalty costs are based on management estimates until new rates are determined.
In 2022, the Copyright Royalty Board began setting rates for the 2023-2027 period under the Phonorecords IV Proceedings. Final regulations were adopted in December 2022.
Rights holder agreements often include audit rights, which could lead to additional royalty payments if disputes arise.
Most royalty liabilities are settled shortly after they are incurred, but some may take longer due to uncertainties.
Spotify has arrangements for advance royalty payments or minimum guarantees. Accruals are established when actual costs are expected to be less than guaranteed amounts.
Some agreements include "most favored nation" clauses, requiring additional payments if Spotify pays lower rates to these licensors compared to others.
Spotify's approach to managing these complexities and uncertainties in content licensing and royalty payments is a critical aspect of its business model, impacting its financial operations and cost of revenue. The company continuously evaluates and adjusts its estimates and accruals to reflect the changing landscape of content licensing in the music and podcast industry.
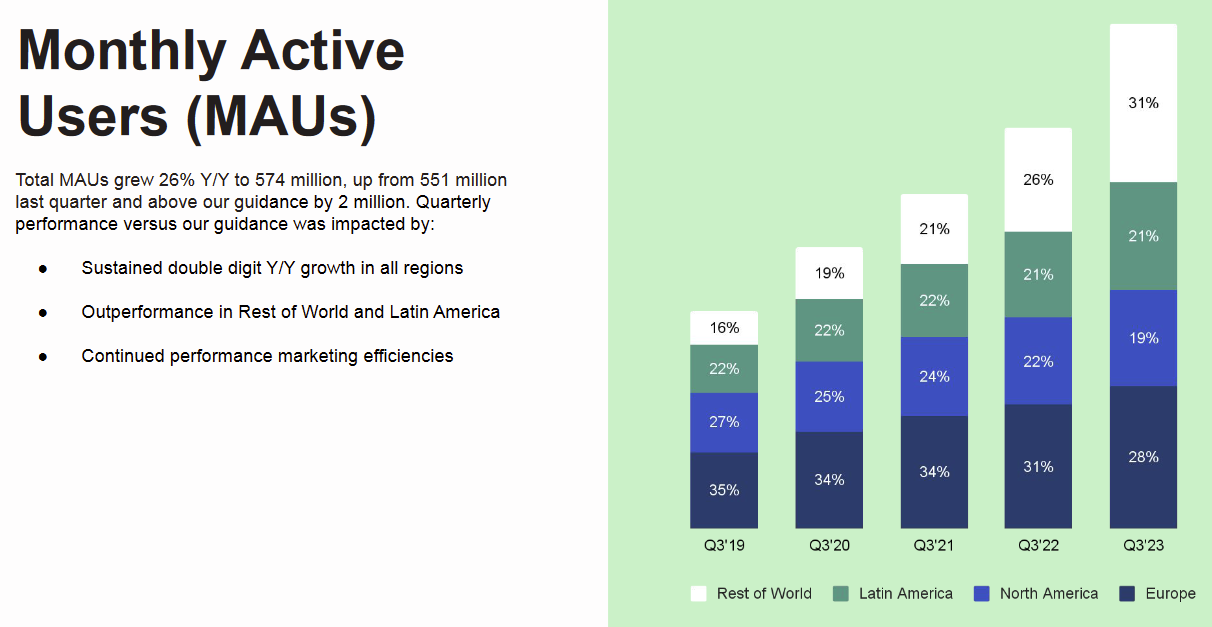
Monthly Active Users
Spotify tracks Monthly Active Users (MAUs) as a key indicator of its audience size and engagement. MAUs are defined as the total count of Ad-Supported Users and Premium Subscribers who have consumed content for more than zero milliseconds in the last 30 days of the period.
Spotify employs several key performance indicators (KPIs) to monitor and manage its business, including Monthly Active Users (MAUs), Premium Subscribers, Ad-Supported MAUs, and Premium Average Revenue Per User (ARPU). These KPIs are essential for evaluating the company's performance, identifying trends, and making strategic decisions.
MAUs:
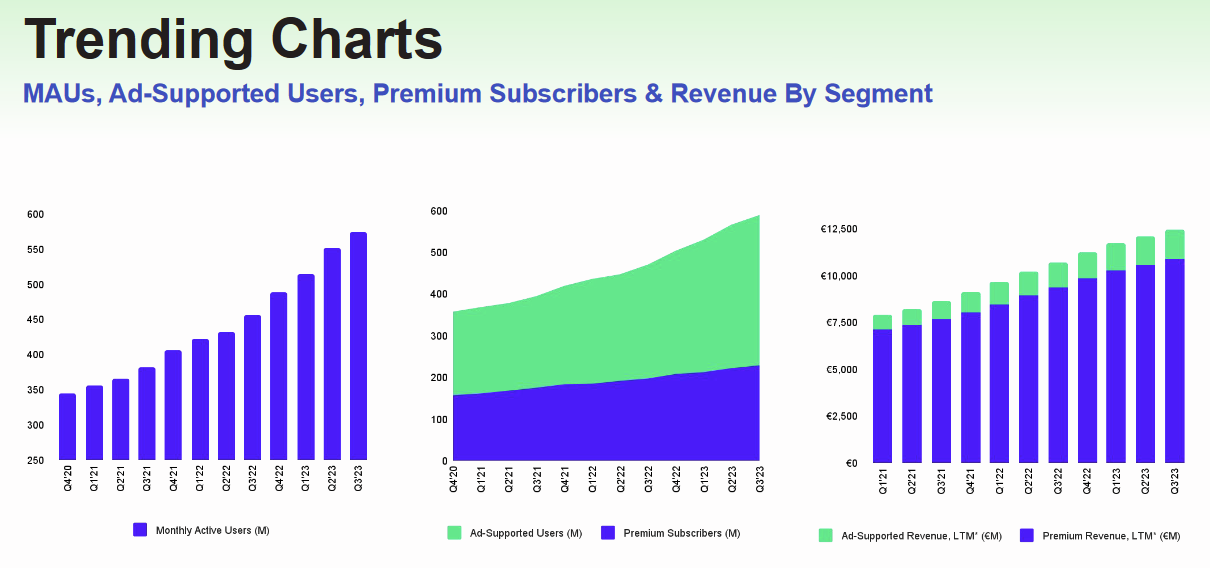
As of September 30, 2023, Spotify's MAUs reached 574 million, marking a 26% increase from 456 million in 2022. This growth is attributed to successful marketing campaigns, enhanced content offerings, and product improvements, leading to sustained user engagement and satisfaction.
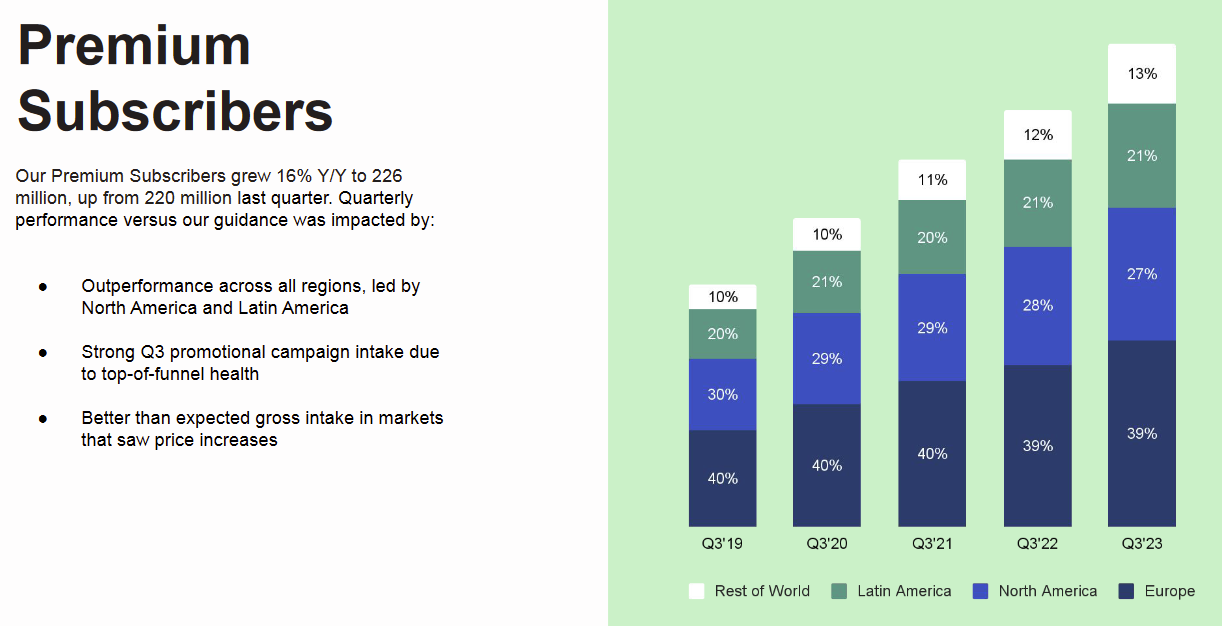
Premium Subscribers:
Premium Subscribers, who have registered and activated a payment method for the Premium Service, increased to 226 million in 2023, up 16% from 195 million in 2022. The growth was significantly driven by free trial offers, global campaigns, and the popularity of the Family and Duo Plans.
Ad-Supported MAUs:
Ad-Supported MAUs, representing users of Spotify's free service, grew to 361 million in 2023, a 32% increase from 273 million in 2022. This increase resulted from ongoing investments in the Ad-Supported Service, effective marketing strategies, and continuous enhancement of content and products.
Premium ARPU:
Premium ARPU for the three months ending September 30, 2023, was €4.34, a decrease of 6% from €4.63 in the same period in 2022. For the nine months ending September 30, 2023, Premium ARPU was €4.31, down 5% from €4.52 in 2022. The decrease is primarily attributed to unfavorable movements in foreign exchange rates and changes in product and market mix.
These indicators provide valuable insights into Spotify’s audience engagement, subscription growth, revenue from Premium users, and the performance of its Ad-Supported segment. They are crucial for assessing the company's operational success and future growth prospects.
Financials
Revenue
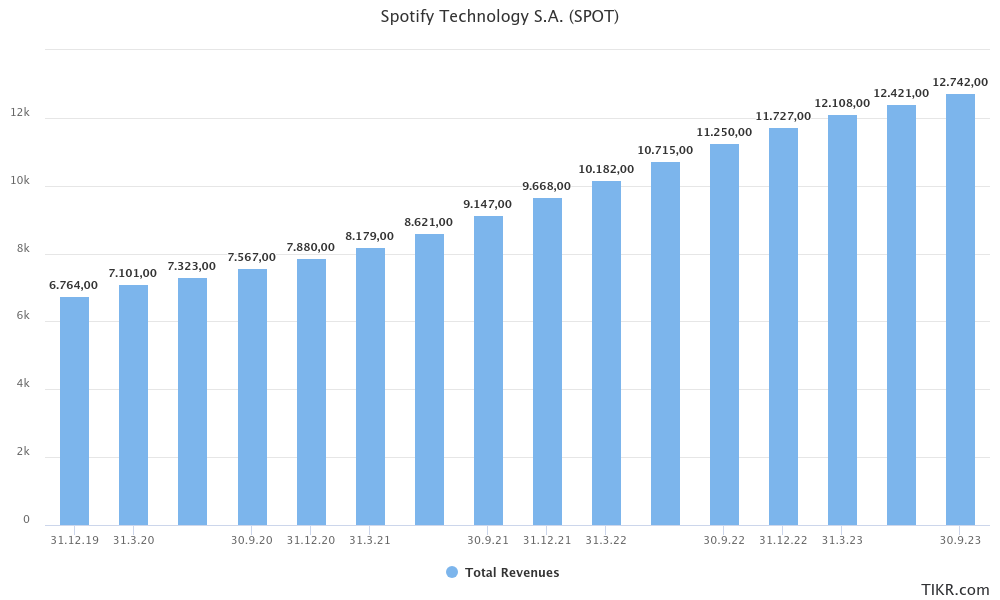
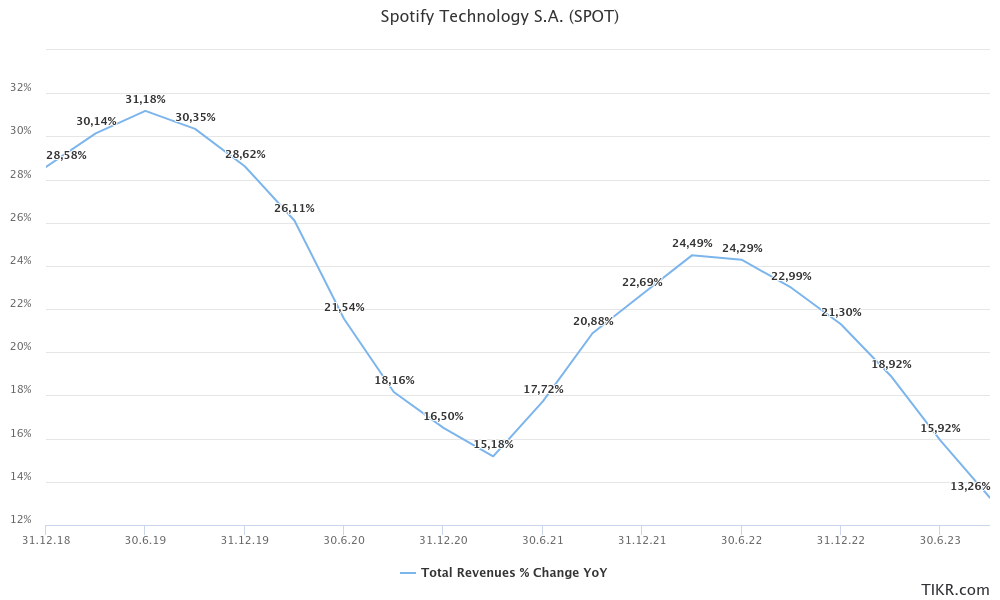
Since 2019, Spotify has experienced a consistent increase in total revenue, achieving a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of approximately 17.1% through Q3 2023, bringing its revenue to $12.7 billion USD. This upward trend is expected to continue, with projections suggesting the total revenue for the entire year of 2023 will reach around $13.3 billion USD. Analysts predict further growth, estimating Spotify’s revenue could rise to about $17.5 billion USD by 2025.
However, it's important to note a shift in the pattern of this revenue growth. Since Q2 2022, there has been a noticeable deceleration in the rate of revenue increase. This trend can be partially attributed to the economic aftermath of the COVID-19 pandemic. Initially, the crisis led to a decline in revenue growth, which was then followed by a robust recovery phase. Currently, the global economic environment, characterized by high inflation rates, rising interest rates, and overall economic uncertainty, appears to be exerting a dampening effect on Spotify’s revenue growth.
This dynamic reflects the broader economic challenges faced by many industries, indicating that while Spotify continues to grow, it is not immune to the macroeconomic factors affecting the global market.
Gross Margin
Gross Margin is usually defined as revenues minus cost of sales or cost of revenue, like Spotify is calling it in his reports. The cost of revenue of Spotify primarily comprises royalty and distribution costs associated with content streaming. These costs break down into several key areas:
Royalty Costs: Paid to record labels, music publishers, and other rights holders for streaming music. These costs are calculated monthly and vary based on several factors:
For the Premium Service, royalties are either a percentage of revenue or a per-user amount, whichever is greater.
For the Ad-Supported Service, they are typically a percentage of relevant revenue, with some agreements also considering the number of streams.
Lower per-user royalty rates have been negotiated for lower-priced subscription plans like the Family, Duo, and Student plans.
Royalties may vary by country and are often contingent on meeting specific targets, such as the number of Premium Subscribers or the ratio of Ad-Supported Users to Premium Subscribers.
Some agreements require advance payments or minimum guaranteed amounts, although incremental costs from these have not been significant to date.
"Most favored nation" agreements may necessitate additional costs if terms are not as favorable as those agreed with other licensors.
Discounts and Promotional Activities: Cost of revenue also reflects discounts given by rights holders for promotional activities related to marketplace programs.
Podcast Content Assets: Costs include the amortization of both produced and licensed podcast content, calculated over the shorter of the content's estimated useful life or the license period. Payments to podcast publishers for content monetized through advertising are also included.
Additional Costs: Other elements contributing to the cost of revenue include credit card and payment processing fees for subscriptions, customer service, employee compensation and benefits, cloud computing, streaming, and costs related to facilities and equipment.
Overall, the cost of revenue for a streaming service like Spotify is complex and multifaceted, reflecting the variety of content and services offered, as well as the diverse agreements and payment structures involved in streaming content to users.
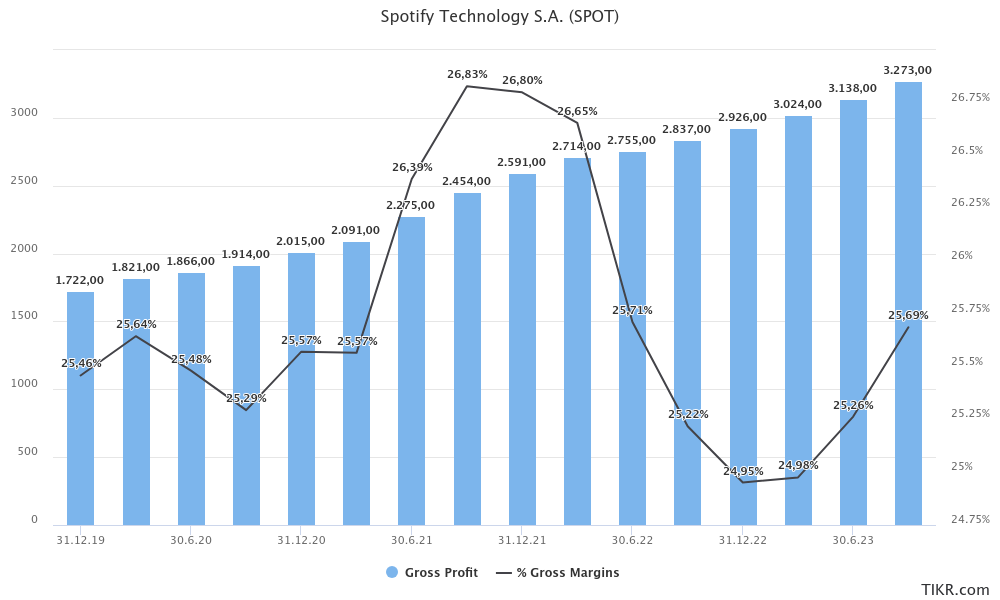
Understanding the gross margin development of Spotify is crucial for assessing its overall profitability. While the company's gross profit in absolute terms has been consistently rising alongside its revenue, the gross margin – representing gross profit as a percentage of revenue – has shown a more static trend, fluctuating within a narrow range of approximately 25% to 27%.
Recently, there has been a noticeable recovery in Spotify's gross margin from its lows at the end of 2022 and the start of 2023. However, this uptick does not yet signify a definitive positive trend or a clear indication of sustained improvement.
Considering Spotify's royalty structures, which are generally tied to revenue and streaming hours, it is evident that increased user engagement, a growing subscriber base, and rising revenues will inherently lead to higher costs of revenue. This relationship suggests that, while growth in these areas is beneficial for the company's top line, it simultaneously exerts upward pressure on the cost of revenue, impacting the gross margin. Therefore, effectively managing these costs while enhancing revenue streams will be critical for Spotify to improve its gross margin and, consequently, its overall profitability.
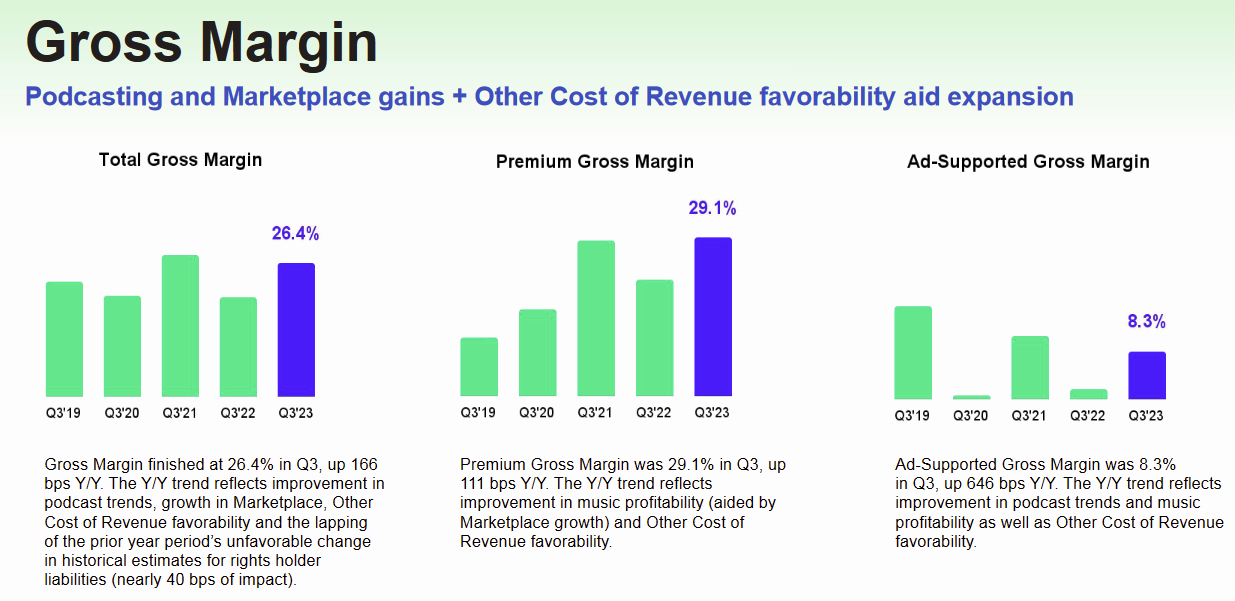
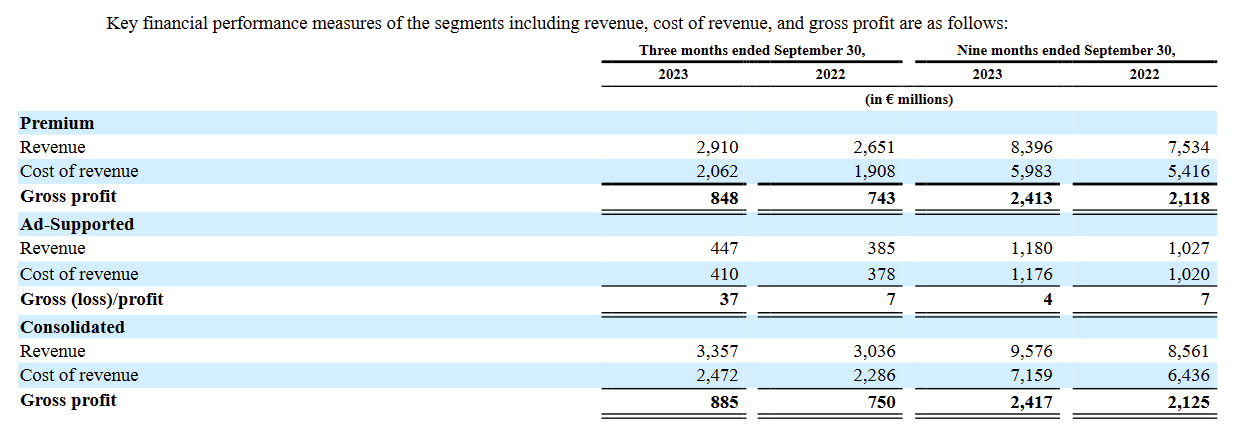
Gross margin varies distinctly between Spotify's Ad-Supported and Premium Subscriber segments, with the Ad-Supported business exhibiting a notably lower gross margin. This disparity highlights a crucial aspect of Spotify's business model: Ad-supported users, on their own, contribute minimally to Spotify's profitability. Rather, their role is more strategic in the company's broader business framework. The primary objective with Ad-Supported users is to first engage them with the service and subsequently encourage their transition into paying Premium subscribers.
In terms of the absolute financial contribution of these two business models for the first nine months of 2023, the difference is stark. The Premium segment accounts for a substantial portion of Spotify's profitability, contributing approximately 99% of the company's gross profit and about 88% of its total revenue. This significant contribution underscores the pivotal role that Premium subscribers play in driving Spotify's financial success, highlighting the necessity of not only maintaining but also growing this segment to ensure sustained revenue and profit growth.
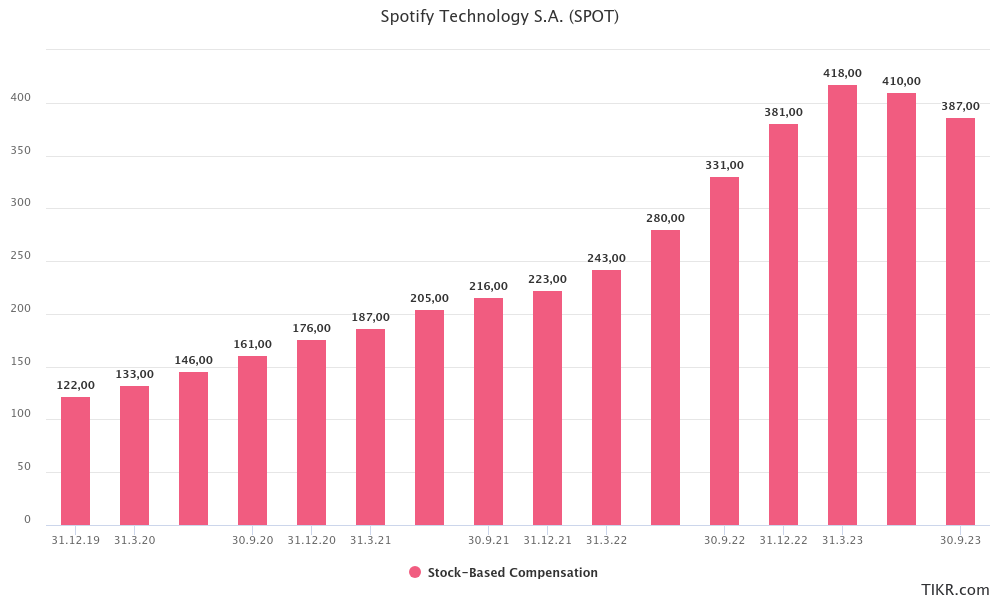
Stock based compensation
In 2020 and 2021, the Company implemented new share-based compensation plans, including Employee Stock Option Plans (ESOP) and Director Stock Option Plans. These plans involve granting stock options to employees and board members, with the exercise price being either the fair market value of shares on the grant date or 150% of this value. These options, denominated in USD, vest over periods of three to eight months and have a five-year term.
Additionally, the Company introduced Restricted Stock Unit (RSU) programs for employees and board directors. The RSUs, measured at the fair market value of shares at grant date, vest over three to eight months initially and fully over four years.
The Company also issued Restricted Stock Awards (RSAs) to employees of acquired companies, vesting over two to three years based on continued employment. For acquisitions like Anchor and The Ringer, equity instruments representing ordinary shares were granted, vesting over four to five years. The fair value of these instruments was determined at the time of grant.
Finally, in the acquisition of Podsights in 2022, the Company granted equity instruments to its employees, with a four-year vesting period based on continued employment. These instruments' values were also determined at the grant date.
These share-based compensation initiatives are part of the Company's strategy to align the interests of employees and directors with the company’s performance and growth.
Spotify's approach to employee compensation prominently features stock-based compensation (SBC), which represents a significant expense, at times exceeding 3% of total sales. This method of compensation, integral to Spotify's strategy for attracting and retaining talent, is likely to persist as a key element of their financial structure. Consequently, investors and analysts should consider the impact of these relatively high SBC expenses on Spotify's overall financial performance.
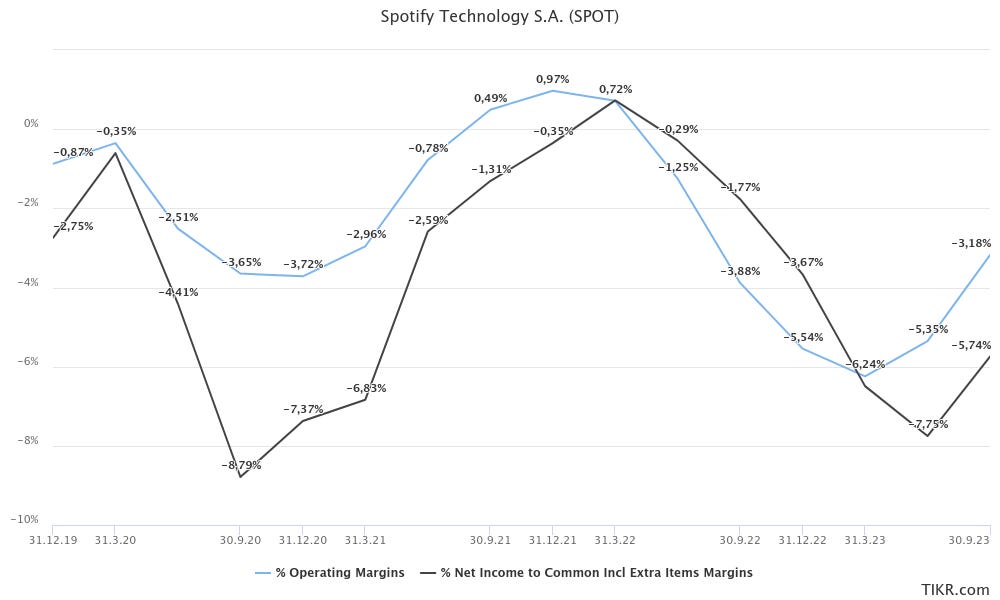
Profitability
Overall, Spotify's profitability tends to track closely with its revenue trends, largely driven by the growth in Premium members who contribute to higher gross margins. However, despite this positive influence from the Premium segment, the company’s overall profit margin appears constrained, leading to a continued lack of profitability.
Consequently, Spotify's net income remains negative. While there has been an improvement in financial results recently, primarily due to increased interest income, these gains are partially negated by negative fair value movements in exchangeable notes and derivatives. This situation underscores the financial complexities Spotify faces, where positive developments in certain areas are offset by challenges in others.
This dynamic illustrates the need for a balanced approach in financial management for Spotify. While revenue growth from Premium subscribers is a strong driver, it needs to be complemented with effective control of costs and liabilities to steer the company towards sustained profitability. The interplay of these financial factors is critical in shaping Spotify's overall economic health.
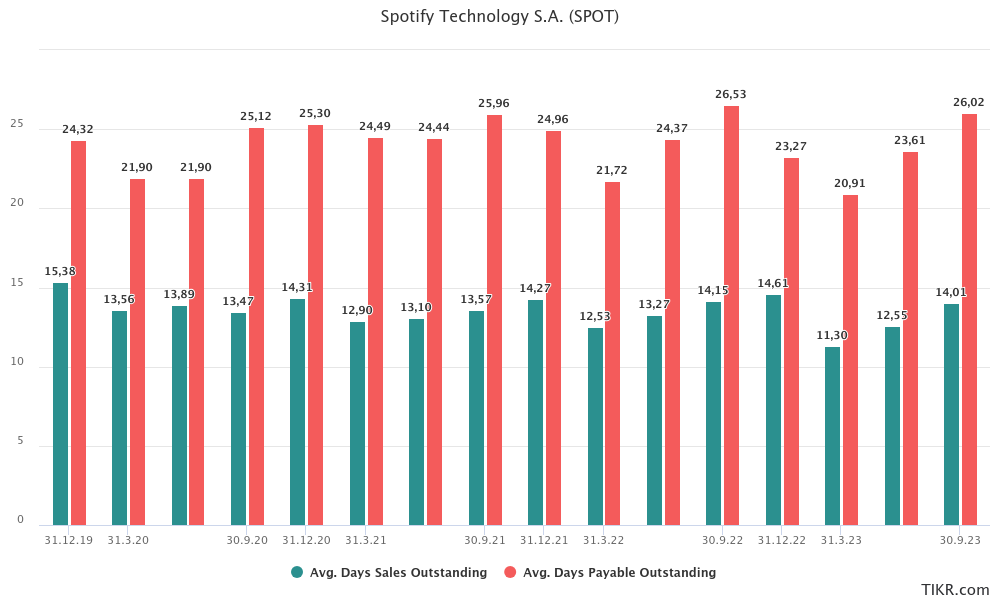
Cash flow profile
Despite facing challenges in achieving profitability in terms of GAAP (Generally Accepted Accounting Principles) income, Spotify's business model successfully generates positive cash flows, primarily attributed to its effective cash flow profile. A key aspect of this is Spotify's highly favorable cash conversion cycle, currently standing at approximately -12 days. This negative cycle (which is positive in financial terms) indicates that the company receives payments from its subscribers several days before it needs to settle its own payables.
This 12-day window presents a strategic financial advantage for Spotify. During this period, the company can actively deploy the incoming funds into the business, either for operational investments or in interest-bearing short-term investments. This efficient management of the cash conversion cycle contributes significantly to Spotify's positive operating and free cash flows, underscoring the company's ability to maintain liquidity and invest in growth even while navigating the challenges of achieving GAAP profitability.
This 12-day window presents a strategic financial advantage for Spotify. During this period, the company can actively deploy the incoming funds into the business, either for operational investments or in interest-bearing short-term investments. This efficient management of the cash conversion cycle contributes significantly to Spotify's positive operating and free cash flows, underscoring the company's ability to maintain liquidity and invest in growth even while navigating the challenges of achieving GAAP profitability.
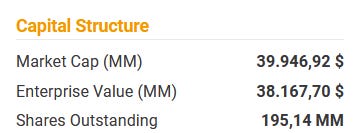
Valuation
Conducting a Discounted Cash Flow (DCF) analysis for a company like Spotify presents significant challenges, primarily due to the high level of forecast uncertainty. The lack of a reliable track record makes it difficult to base assumptions about future profitability, rendering any DCF results potentially misleading. Given this unpredictability, relying on a DCF model for Spotify might be akin to 'crystal ball gazing', with results varying widely within a large range. This high degree of uncertainty makes it nearly impossible to provide a credible estimation of the company's fair value using this method.
Similarly, applying a multiplier valuation method also poses difficulties. Valuation metrics based solely on sales are often not preferred in such scenarios, especially when earnings and cash flow metrics are not sufficiently reliable. Given Spotify’s stagnating profitability and in Free Cash Flow (FCF) generation, these methods could lead to the conclusion that the company's stock is currently overvalued.
In essence, traditional valuation methods like DCF and multiplier-based approaches encounter significant hurdles when applied to companies like Spotify, where financial predictability is limited and growth prospects are uncertain. This necessitates a more nuanced approach to valuation, taking into account the unique aspects of Spotify's business model and market dynamics.
Investment Thesis
Shareholder Structure
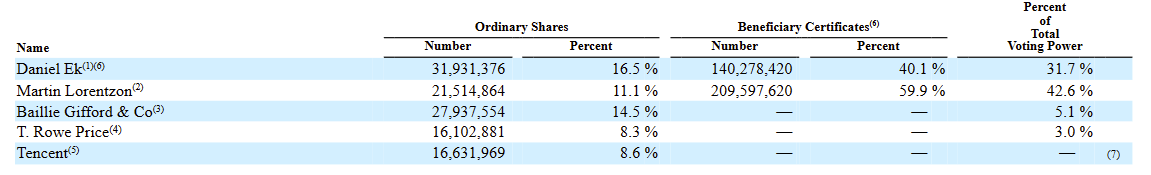
The unique ownership structure of Spotify, where founders Daniel Ek and Martin Lorentzon hold a majority in voting power, presents both advantages and potential drawbacks. This concentrated control can be beneficial, particularly because Ek and Lorentzon have a strong focus on product development, technology, and audio content. Their vision and deep understanding of the industry can drive innovation and maintain the company's competitive edge in a rapidly evolving market.
However, this concentration of voting power also brings certain challenges, particularly in the realm of financial ambitions. There may be instances where the company's strategic financial decisions could benefit from a broader range of perspectives, especially in areas like profitability, revenue growth, and cost management.
Notably, Daniel Ek exercises significant influence over the company through his indirect ownership of D.G.E. Investments. This entity holds an irrevocable proxy regarding the ordinary shares of TME Hong Kong, Image Frame, Tencent Mobility Limited, and Distribution Pool Limited. Such an arrangement solidifies his control over key decisions and directions for Spotify, which, while ensuring consistency in vision and strategy, may also limit the diversity of input in critical decision-making processes.
This governance structure emphasizes the importance of balancing visionary leadership with financial prudence. For Spotify to continue thriving, it will be crucial for its leadership to integrate financial objectives seamlessly with their technological and content-focused ambitions, ensuring sustainable growth and shareholder value in the long term.
Investor Day 2022 highlights
The 2022 Spotify Investor Day offered a glimpse into the company's ambitious financial aspirations, yet these goals warrant a cautious and critical examination. CEO Daniel Ek articulated a vision of substantial growth, aiming to transform Spotify from its music streaming origins into a comprehensive audio platform encompassing podcasts and audiobooks.
Financially, Spotify sets its sights high, targeting a staggering 25-35% annual revenue growth and aspiring to a gross margin of 30-35%. This optimism is primarily fueled by the anticipated high margins in emerging verticals like podcasts and audiobooks. However, the practicality of these targets, particularly in a competitive and rapidly evolving digital media landscape, could be questioned. The podcast sector, though promising, is still in its investment phase, and its future profitability, pegged at a gross margin potential of 40-50%, remains speculative.
Ek's projection of achieving $100 billion in revenue, reaching 1 billion users, and attaining a 40% gross margin and a 20% operating margin is notably bold. These figures, while reflecting confidence in Spotify's strategic direction, also underscore the monumental scale of growth and efficiency improvements required. Such goals, especially in the context of Spotify's current financial standing and market dynamics, may seem overly optimistic, if not overly ambitious.
Moreover, the strategy of diversifying revenue streams beyond music streaming royalties – through promotional tools, live audio features, merchandising, and concert ticket sales – presents its own set of challenges. While these initiatives could contribute to revenue growth and margin improvement, their success is not guaranteed and will depend on Spotify's ability to innovate and compete effectively.
In summary, while Spotify's financial goals outlined during the Investor Day are grand and reflect a forward-thinking approach, they should be approached with a degree of skepticism. The journey towards these targets will likely encounter numerous challenges, including market competition, evolving consumer preferences, and the inherent uncertainties of scaling new business verticals. As such, these ambitious plans warrant careful observation and critical analysis as Spotify navigates its path forward in the dynamic world of digital audio entertainment.
Growing audience
Audio entertainment, especially music, holds a significant place in human culture and daily life. The widespread love for music, coupled with the growing popularity of podcasts and audiobooks, underscores why the number of active users in these domains is on a steady rise. This trend doesn’t show signs of slowing down, and it's reasonable to anticipate further growth in the foreseeable future. Predicting the ultimate reach or ceiling of this growth is challenging, but the potential for expansion in the audio entertainment sector is undeniable.
The Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 29.31% from 68 million users in Q1 2015 to 574 million in Q3 2023 is a testament to this growth, amounting to an impressive total increase of 744%. Even more remarkable is the 1156% surge in Premium Subscribers during this period. These figures not only reflect the increasing global appetite for audio content but also highlight the vast potential and dynamism of the audio entertainment industry. As user preferences evolve and new formats emerge, the industry is poised to continue this upward trajectory, tapping into the deeply ingrained human connection to music and spoken word content.
Complex revenue and royalty model
The current landscape of the audio streaming industry, particularly for companies like Spotify, presents complex financial challenges that could impact future profitability. One of the imminent challenges is the potential for price hikes, which, while possibly boosting revenue, also come with the risk of increasing royalty costs. This dynamic creates a delicate balance for Spotify in managing its revenue streams and cost structure.
Furthermore, the intricacies of Spotify's revenue model, coupled with the complexities inherent in its royalty and licensing agreements, present substantial hurdles in significantly improving its gross margin. These agreements, often based on a combination of revenue percentages and per-user or per-stream rates, create a financial structure where increased usage can lead to proportionally higher costs. This scenario complicates efforts to expand margins, as rising revenues can simultaneously escalate expenses.
Currently, envisioning a path for Spotify to consistently achieve a gross margin above 30% is challenging. The interplay between revenue growth, pricing strategies, and royalty obligations forms a complex web that dictates the company’s gross margin. Any strategy to enhance profitability must consider not only the revenue side of the equation but also the intricate cost dynamics, including royalty payments which constitute a significant portion of the company's expenses.
To improve gross margins, Spotify may need to explore innovative approaches to its business model. This could involve renegotiating licensing terms, diversifying revenue streams beyond traditional music streaming, or investing in original content with more favorable cost structures. Additionally, enhancing user engagement and loyalty through personalized experiences and exclusive content might allow for more flexible pricing strategies, potentially offsetting some of the pressures on margins.icensee agreements make it hard to improve gross margin significantly. At the moment hard to see a gross margin over 30%.
Investment in Tencent Music
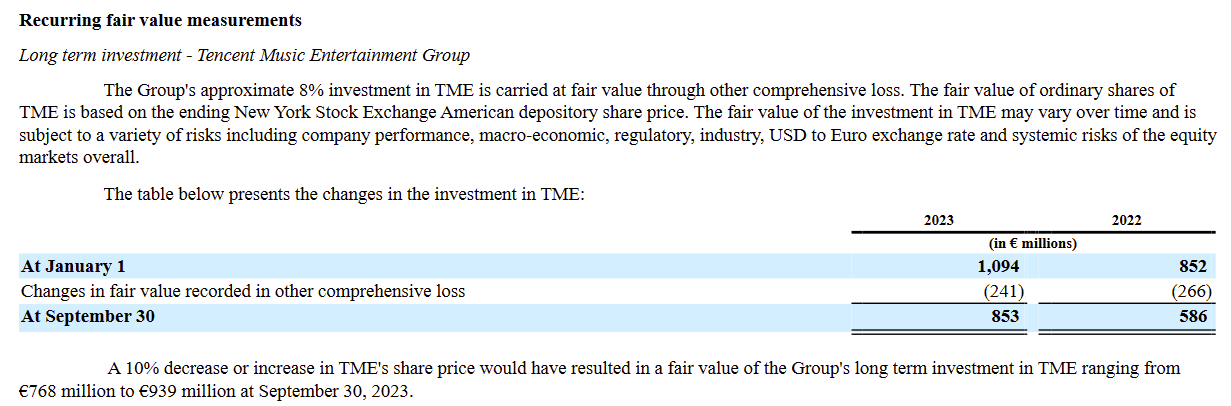
Spotify's long-term investment in Tencent Music Entertainment Group (TME), approximately an 8% stake, presents both opportunities and challenges. This investment, carried at fair value through other comprehensive loss, is evaluated based on the fluctuating New York Stock Exchange American depository share price. While this strategic alliance could open doors to lucrative markets and collaboration opportunities, particularly in the expansive and evolving Chinese music and entertainment sector, it is not without its risks.
The fair value of this investment is susceptible to a myriad of factors. These include TME's individual performance, broader macroeconomic conditions, regulatory changes, and the dynamics of the music and entertainment industry. Additionally, the USD to Euro exchange rate and systemic risks inherent in equity markets significantly impact the investment's value.
One critical point to consider is the regulatory environment in China, which can be unpredictable and could pose significant challenges for foreign investors. Changes in regulations or shifts in the political landscape could affect TME’s operations and, consequently, the value of Spotify's investment.
However, on the flip side, this investment offers Spotify a unique opportunity to tap into the Chinese market, which is vast and has a burgeoning digital music scene. It could provide Spotify with valuable insights into consumer preferences and trends in the region, potentially informing its global strategy. Additionally, as TME continues to grow and potentially diversify its offerings, Spotify stands to benefit from the financial returns of this investment and the strategic partnerships that may arise.
In essence, while the investment in TME carries inherent risks, particularly due to external market and regulatory factors, it also holds the potential for significant strategic and financial benefits for Spotify. This delicate balance makes it a noteworthy aspect of Spotify's investment portfolio, requiring careful monitoring and strategic foresight.
Conclusion
Spotify stands as a remarkable European company with a significant global presence, renowned for its influential brand and platform in the music industry. Its massive audience, deeply ingrained in the cultural fabric of music, holds the potential to expand even further. While Spotify operates in a competitive landscape with formidable rivals like Apple Music and Amazon Music, it distinguishes itself through an exceptional user experience and a vast, diverse content library.
Despite its growth and industry impact, Spotify faces challenges. The company's growth rate has shown signs of slowing, and achieving profitability remains a hurdle. Margin expansion is particularly challenging, given the nature of Spotify's business model, which involves complex royalty and licensing agreements. These agreements, essential for offering a broad range of music and audio content, also contribute to the company's significant cost structure.
Notably, Spotify has had a profound impact on the music industry, especially for independent artists. It has democratized music publishing, allowing artists to independently release their music and audio content, thereby reshaping the industry's dynamics.
From an investment perspective, 2023 has been favorable for Spotify shareholders, reflecting positively in stock performance. However, valuing the company remains a complex task. Based on current financials, the stock appears to be overvalued, suggesting a mismatch between market expectations and the company's financial realities. Predicting whether Spotify will grow into its high valuation is challenging, particularly in the short term. Investors considering Spotify must weigh the company's influential market position and potential for future growth against the financial uncertainties and competitive pressures it faces.
Disclaimer: The information provided in this publication is for educational and informational purposes only and does not constitute financial advice. The content is solely reflective of my personal views and opinions based on my research and is not intended to be used as a basis for investment decisions. While every effort is made to ensure that the information is accurate and up-to-date, the writer makes no representations as to the accuracy, completeness, suitability, or validity of any information in this post and will not be liable for any errors, omissions, or delays in this information or any losses, injuries, or damages arising from its display or use. All readers are advised to conduct their own independent research or consult a professional financial advisor before making any investment decisions. The author is not invested in SPOT .